Thermal energy plays a key role in our everyday lives, yet many people don’t fully grasp what it is or how it works. This form of energy originates from the motion of tiny particles within substances. It’s what makes things warm or hot, and it’s behind processes like boiling water, cooking food, and even powering engines. In simple terms, thermal energy is the energy generated by heat, and it’s closely tied to the movement of particles inside objects.
So, why does thermal energy matter? Understanding this concept helps explain how heat moves from one place to another and how it can be used to perform work. Whether you’re trying to figure out why your coffee cools down over time or how a power plant generates electricity, thermal energy is at the heart of it all. It’s one of the fundamental forms of energy that we interact with daily, often without realizing it.
By the way, did you know that thermal energy isn’t just about the heat you feel? It’s also about the hidden energy within objects, which includes both the movement of particles and their interactions. This energy can be converted into other forms, like mechanical or electrical energy, making it incredibly versatile. Let’s explore what thermal energy really means and how it affects the world around us.
What Exactly is Thermal Energy?
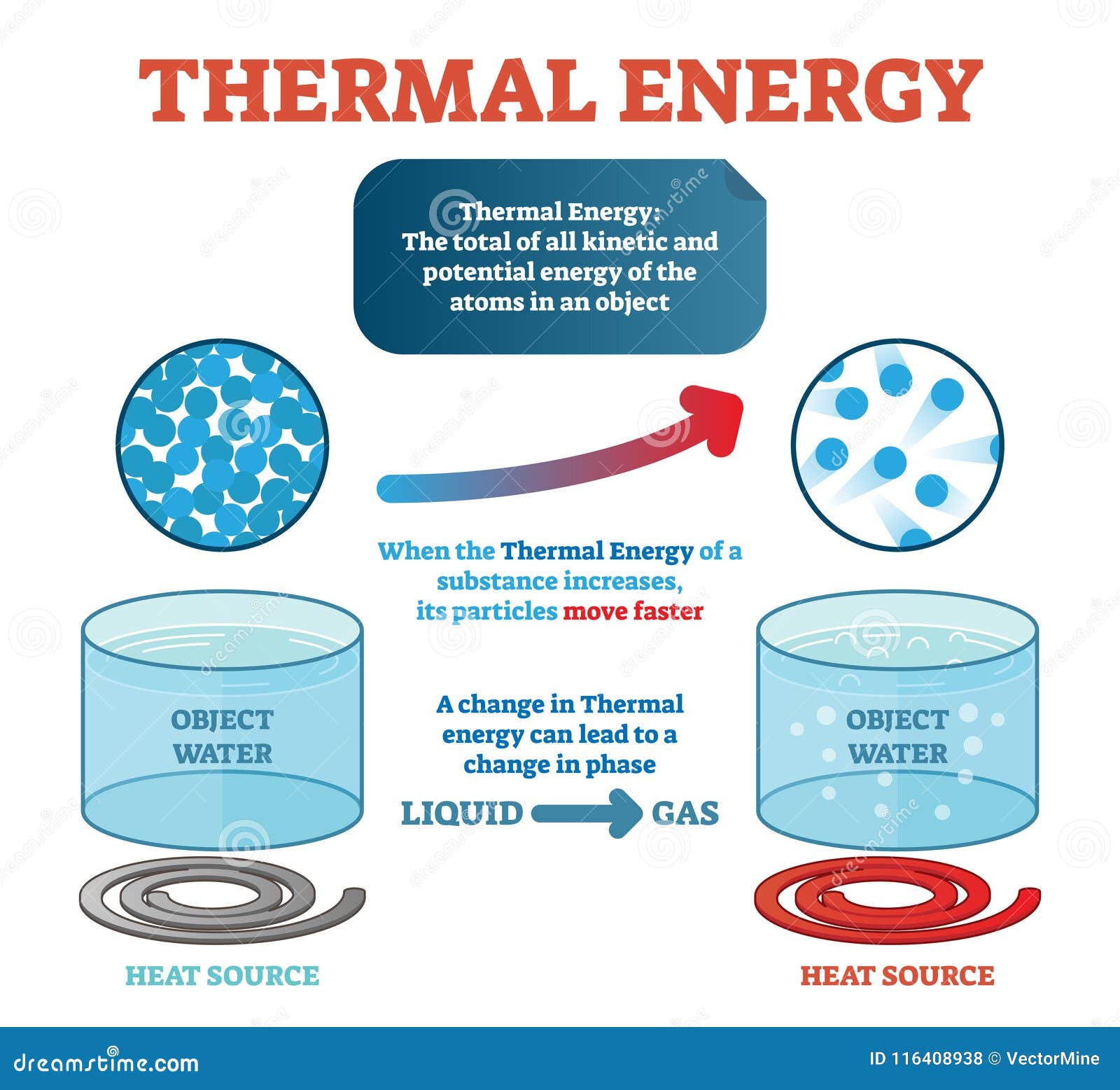
Alright, let’s break it down. Thermal energy is essentially the energy that comes from the temperature of a heated substance. It’s all about the movement of particles—whether they’re vibrating, rotating, or moving around. Every object you see, from the tiniest pebble to the biggest mountain, is made up of super small particles called atoms. These atoms are always moving, and the faster they move, the more thermal energy the object has.
In some respects, thermal energy is like the invisible fuel that drives many processes. For example, when you touch a hot stove, the heat you feel is the transfer of thermal energy from the stove to your hand. Similarly, when you boil water, the thermal energy from the burner causes the water molecules to vibrate faster, eventually turning the liquid into steam.
How is Thermal Energy Produced?
Thermal energy is produced when particles within an object start moving faster due to an increase in temperature. Think of it this way: imagine a bunch of tiny marbles bouncing around in a box. If you shake the box harder, the marbles move faster and bump into each other more often. In the same way, when an object heats up, its particles gain energy and move more quickly.
This movement generates what we call thermal energy. Sometimes, it’s easy to see, like when something gets hot to the touch. Other times, it’s hidden, like the internal energy within the particles themselves. Either way, thermal energy is always there, even if you can’t always feel it.
What is the Difference Between Thermal Energy and Heat?
People often use the words “thermal energy” and “heat” interchangeably, but they’re not exactly the same thing. Thermal energy is the actual energy a substance or object’s particles have because of their motion. Heat, on the other hand, is the transfer of this energy from one place to another.
For instance, when you place a pot of water on a stove, the stove transfers heat to the water, increasing its thermal energy. The water molecules start moving faster, and the temperature rises. So, while thermal energy is the energy stored in the object, heat is the process by which that energy moves.
What is Thermal Energy - An Everyday Example
Let’s take a closer look at how thermal energy works in everyday situations. For example, a cup of hot tea has thermal energy in the form of kinetic energy from its vibrating particles. The hotter the tea, the faster the particles move, and the more thermal energy it contains. As the tea cools down, the particles slow down, and the thermal energy decreases.
This simple example shows how thermal energy affects the things we interact with daily. It’s not just about the tea, though. The same principle applies to your car engine, your home heating system, and even the sun. All of these rely on thermal energy to function.
Why Does Temperature Matter?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. It tells you how fast the particles are moving on average. So, when you say something is hot, you’re really saying that its particles are moving very fast. Conversely, if something is cold, its particles are moving more slowly.
This relationship between temperature and thermal energy is crucial. The higher the temperature, the more thermal energy an object has. That’s why boiling water has more thermal energy than lukewarm water. It’s all about the speed and motion of those tiny particles.
What is Thermal Energy - Can It Be Converted?
Thermal energy can indeed be converted into other forms of energy. For example, in a power plant, the thermal energy from burning coal is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. This is a common way of converting thermal energy into mechanical energy, which can then be turned into electrical energy.
However, not all thermal energy can be converted efficiently. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium, like a flowing fluid or a moving solid, don’t always allow for easy conversion. That’s why engineers and scientists are always looking for ways to improve the efficiency of energy conversion processes.
What is the Formula for Thermal Energy?
If you want to calculate thermal energy, there’s a simple formula you can use. It’s based on the concept of heat capacity, which measures how much energy it takes to raise the temperature of an object. The formula is:
Thermal energy input = specific heat capacity × mass × temperature change
For example, if you have a 1-kilogram block of metal and you want to raise its temperature by 10 degrees Celsius, you need to know its specific heat capacity to calculate the thermal energy required. This formula helps scientists and engineers figure out how much energy is needed for various processes.
How is Thermal Energy Related to the Laws of Thermodynamics?
The laws of thermodynamics explain how thermal energy behaves in different situations. The first law, for instance, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This means that the thermal energy in a system can be converted into other forms, like mechanical or electrical energy, but the total amount of energy remains constant.
The second law adds another layer to this by saying that energy naturally tends to spread out or become more disordered over time. This is why heat flows from hot objects to cold ones and not the other way around. These principles help us understand how thermal energy works in the real world.
What is Thermal Energy - Is It Always Visible?
Sometimes, thermal energy is obvious, like when you feel the warmth of the sun on your skin. Other times, it’s hidden, like the internal energy within the particles of an object. This “hidden” energy includes both the kinetic energy of moving particles and the potential energy of their interactions.
For example, a block of ice may feel cold to the touch, but it still contains thermal energy. The particles inside the ice are moving, just not as fast as those in a hot object. This hidden energy is what makes thermal energy so fascinating—it’s always there, even when you can’t see or feel it.
What Are Some Applications of Thermal Energy?
Thermal energy has countless applications in our daily lives and in various industries. It’s used to heat homes, cook food, power vehicles, and generate electricity. For instance, in a car engine, the thermal energy from burning fuel is converted into mechanical energy to move the vehicle.
Similarly, in power plants, thermal energy is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Even in something as simple as a toaster, thermal energy is at work, heating up the bread to make it crispy and golden.
So, whether you’re enjoying a warm cup of coffee or driving to work, thermal energy is playing a key role. It’s a fundamental part of how the world works, and understanding it can help us make better use of the energy resources around us.
Summary
Thermal energy is the energy that comes from the temperature of a heated substance, generated by the movement of particles within objects. It can be produced, transferred, and converted into other forms of energy, making it incredibly versatile. Understanding thermal energy helps explain how heat moves and how it can be used to perform work. From heating homes to powering vehicles, thermal energy plays a crucial role in our daily lives and in various industries.

Detail Author:
- Name : Mrs. Nyasia Wilkinson
- Username : johns.mallie
- Email : will.andy@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1989-06-07
- Address : 69469 Torphy Loaf Apt. 429 North Ryleymouth, RI 61076
- Phone : 985-636-2587
- Company : Spinka-Jacobs
- Job : Farmworker
- Bio : Nobis voluptate porro quia quas. Dicta recusandae eos aut occaecati necessitatibus. Et quia iusto porro facere.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/wherzog
- username : wherzog
- bio : Distinctio qui ut error excepturi in.
- followers : 4074
- following : 1455
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/wilfredherzog
- username : wilfredherzog
- bio : Explicabo ipsa quisquam qui hic iusto in.
- followers : 740
- following : 378